How to Calculate Your High 3 for Federal Retirement
November 22nd, 2022 | 3 min. read

Upon retirement, the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS) will pay federal workers a monthly benefit based on their years of service worked under FERS, average high 3-year salary and age. This FERS basic benefit is often known as the monthly annuity. It is a major source of retirement income for federal workers. Knowing how it is calculated can help you decide when it’s the right time to retire.
So, let’s break down how to calculate your high 3 for federal retirement.
What is the Average High 3 Salary?
Your high 3 is the average of your highest three consecutive years of basic pay under FERS. These do not need to be calendar years. It’s not uncommon that your highest income years are the last three years you work, but it’s not always the case.
FERS basic benefit formula
In addition to your average high 3 salary, your years of service and retirement age impact the size of your benefit.
FERS pays benefits using the following two formulas based upon your retirement age:
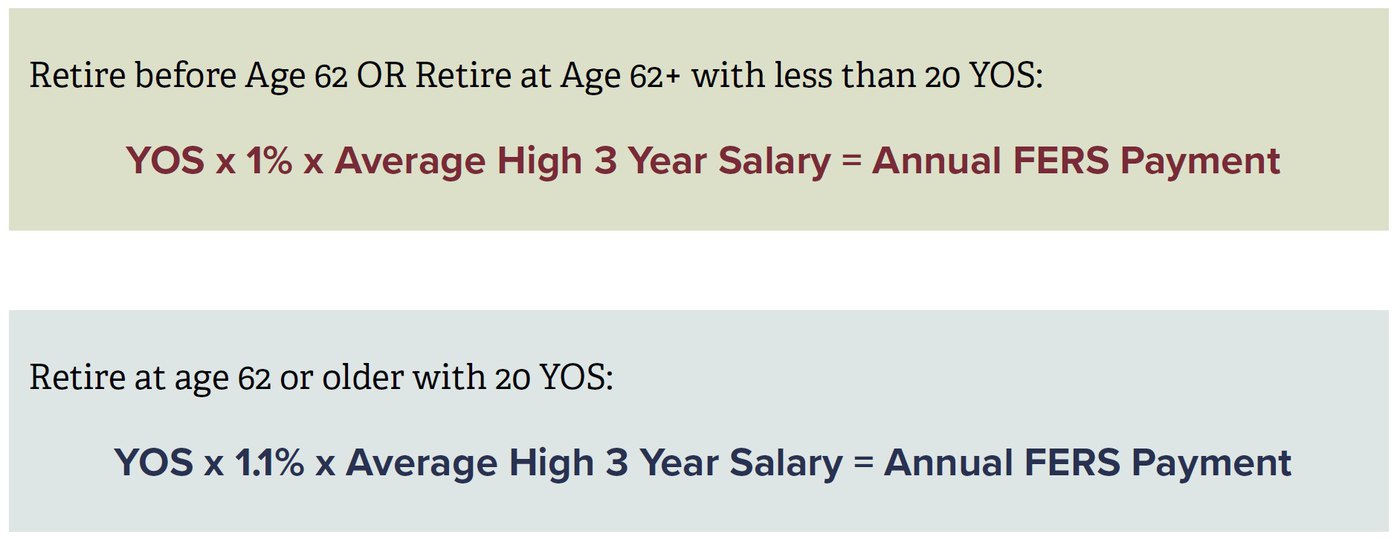
A note on Years of Service (YOS): This is the number of years worked while in FERS. Unused sick leave is converted into days/months for the purpose of crediting additional partial years when determining your time as YOS. Military service is eligible to be bought for additional FERS YOS but is NOT automatically applied – you must elect this conversion. Learn more about your FERS benefit calculation here.
Calculating your high 3 for federal retirement
As you can see above, your average high 3-year salary is multiplied by a certain multiplier based on your retirement age.
Under age 62 at Separation for Retirement, or age 62 or older with less than 20 Years of Service: 1% of your average high 3-year salary for each year of service.
Age 62 or older with at least 20 Years of Service at the date of your Separation for Retirement: your benefit is increased to 1.1% of your average high 3-year salary for each year of service. This bonus is not available for younger retirees regardless of service time and will not switch over at age 62.
As an example, a federal worker who retires at age 60 with 25 YOS and a High 3 of $65,000 (1% x 65,000) would receive a benefit of $16,250 per year. Retiring at age 62 with the same YOS and
High 3 (1.1% x 65,000), the federal worker would receive an increased benefit of $17,875 per year – a permanent 10% increase!
Therefore, a higher-paying position or a raise boosts your average high 3-year salary. This will help you in the near term, as you earn more, and in retirement with a higher benefit payout.
Visit Advance Capital Management's FERS Retirement University to find more helpful articles covering FERS, federal government benefits, TSP investing and more.
Other factors impacting your FERS benefit
Retirement age
There are two eligibility options that affect the size of your basic benefit.
- Unreduced Benefits - To be eligible for unreduced benefits (immediate retirement) you must meet one of the following criteria:
- Must reach Minimum Retirement Age (“MRA”) (age 55-57, depending upon your year of birth) with 30 years of service
- Age 62 with 5 years of creditable service
- Age 60 with 20 years of creditable service
It is possible to retire earlier than your MRA, but that requires circumstances outside of your control such as involuntary separation without cause, reorganization, retirement offers, or disability.
- Early Retirement: Federal workers can be eligible for early retirement if they have reached their MRA and have 10 years of service. Those that elect early retirement will have their basic benefit permanently reduced by 5% for each year they retire before age 62.
Find out the best dates to retire from FERS in this article.
Survivor annuity
There are a couple options available for married retirees that can extend a portion of FERS annuity payments to their surviving spouse. Here are the options:
- Self-Only Annuity: This “single life” annuity will pay the full annuity amount only until the retiree passes – nothing is left for the surviving spouse.
- One-Half Maximum Survivor Benefits: While the retiree lives and receives benefits, the pension amount will be reduced by 5% per month. In exchange, the surviving spouse will receive 25% of the retiree’s full annuity amount after the retiree passes.
- Maximum Survivor Benefits: While the retiree lives and receives benefits, the pension amount will be reduced by 10% per month. In exchange, the surviving spouse will receive 50% of the retiree’s full annuity amount after the retiree passes.
Not sure what options are right for you? Take advantage of our retirement planning services to get help from an FERS retirement benefits expert.
For a personalized calculation of your high 3 for federal retirement and other benefit factors, consider speaking to a financial adviser. An adviser can provide an entirely personalized and comprehensive retirement plan that includes a variety of estimations based on your FERS benefit, TSP plan and all other assets. Further, a professional can suggest different strategies to take that you may not realize are available to you. Click this link to schedule a free financial consultation today!
Learn more about government retirement benefits, including the FERS basic benefit, the Thrift Savings Plan and other retirement planning steps, by downloading our free, easy-to-understand guidebook, FERS Made Simple: Understanding and Maximizing Your Benefit.
As a financial adviser, Kurt takes a comprehensive approach to help clients work toward their financial goals by providing wealth management tools including retirement planning, investment portfolio advice and tax strategies. He specializes in federal government benefits and is a Chartered Retirement Planning Counselor.


